Battery Markup Language (BatML) Standard
Example Models for Batteries
Example 3: Cylindrical Cell (Electrochemical/Electrical/Thermal)
This example (located in VIBE repository at trunk/examples/case3/) contains the same battery components as example 2 in a more complex geometry of a rolled cylindrical cell. The main model properties are given in the table below. Fig. 5 shows the geometry and the finite element mesh used to resolve the geometry of the cylindrical cell and the current collectors. The top hierarchy model has 168 (56 each for the cell-sandwich and positive and negative current collectors) zones in 4 quadrants. The zones describe different current collector and cell sandwich regions. The simulation uses 56 concurrent Dualfoil simulations for different cell-sandwich zones. Typical results are shown in Fig. 6. The maximum temperature occurs at the cell core as expected.
| Physical Properties | Units | Total | Carbon Electrode (Anode) | Lithium Electrode (Cathode) | Al Foil | Cu Foil | Separator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | kg/m3 | 2500 | 1500 | 2700 | 8960 | 1200 | |
| Heat Capacity | J/Kg-K | 700 | 700 | 900 | 385 | 700 | |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/m-K | 0.01 | 0.01 | 238 | 398 | 0.01 | |
| Electrical Conductance | S/m | 0.0051 | 0.0051 | 383x105 | 633x105 | 0.0051 | |
| (rCp) avg | J/m3-K | 175x104 | |||||
| Height | m | 0.05 | |||||
| Diameter | m | 0.02 | |||||
| Current Density | A/m2 | 35 | |||||
| Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient | W/m2-K | 25 |

Figure 5: Geometry and mesh of the simulated cylindrical cell
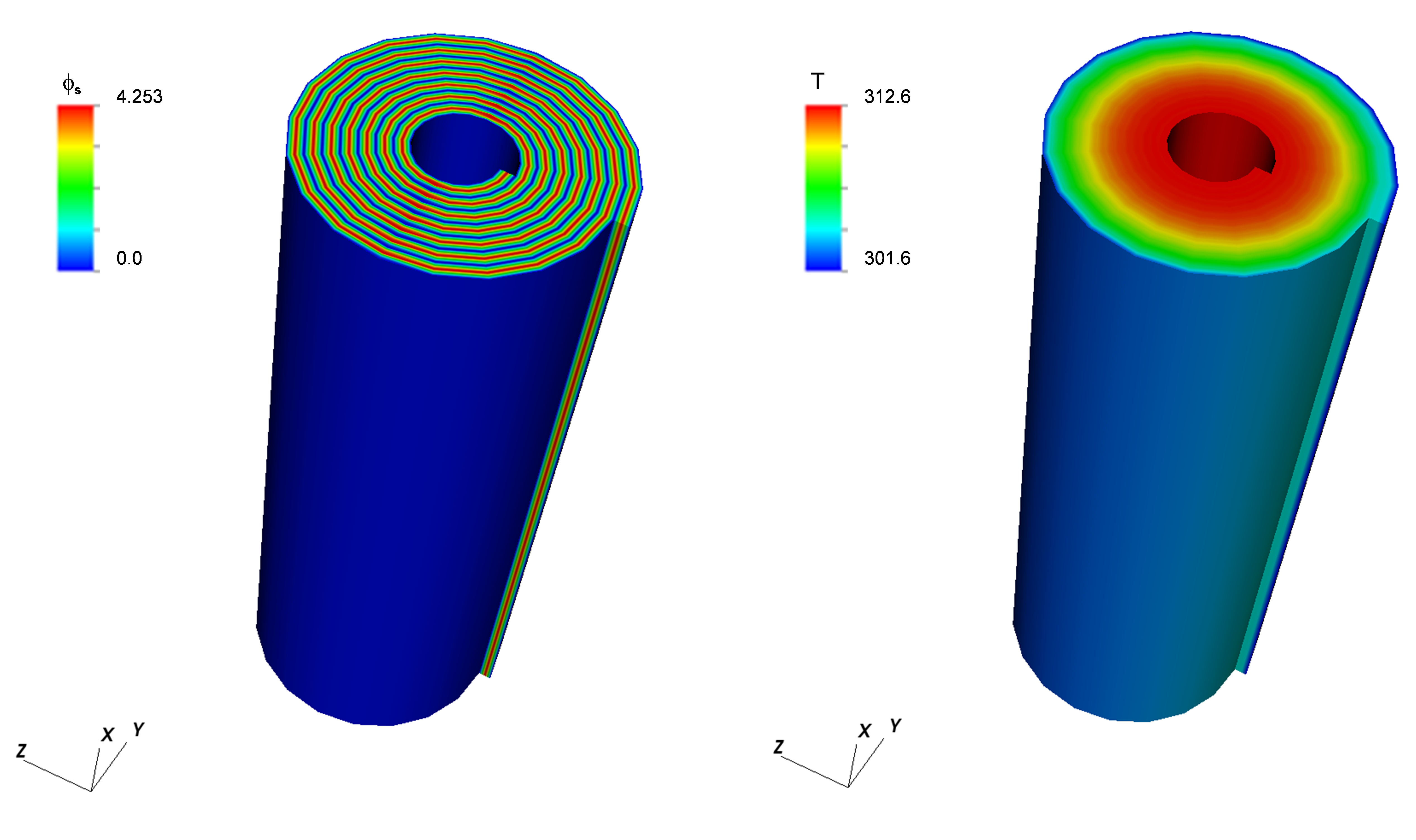
Figure 6: Sample results for example 3 (electrical potential on the left and the temperature on the right)